Pulmonary Embolism Awareness
 Download pdf
Download pdf
 Download pdf
Download pdf
Pulmonary Embolism
We are here to ensure you feel informed, comfortable, and supported throughout your journey. If you have any questions, please speak with your doctor or the medical team.
Understanding a Serious Condition That Needs Fast Action
A Pulmonary Embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks a blood vessel. It can happen suddenly and may be life-threatening if not treated quickly. Knowing the warning signs, risk factors, and when to seek medical help can save your life — or someone else’s.
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
A Pulmonary Embolism is usually caused by a blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the legs (a condition called deep vein thrombosis, or DVT) and then travels to the lungs. This blocks normal blood flow and reduces oxygen in the body.
Recognise the Symptoms — Act Fast
PE symptoms can appear suddenly or develop over hours. Seek immediate medical attention (call 911) if you experience:
- Sudden shortness of breath, even at rest
- Sharp chest pain that worsens when
- breathing deeply or coughing
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Coughing up blood (haemoptysis)
- Feeling lightheaded, dizzy, or fainting
- Sudden unexplained anxiety or sweating.
If you have these symptoms and any risk factors for clots, treat them as an emergency.
Know the Risk Factors
Anyone can develop a Pulmonary Embolism, but your risk increases with:
- Recent surgery or hospital stay (especially involving legs, hips, or abdomen)
- Prolonged immobility — long flights, car journeys, or bed rest
- A history of DVT or PE
- Family history of blood clots
- Pregnancy or recent childbirth
- The use of oestrogen-based medications (like
- the pill or hormone replacement therapy)
- Cancer or cancer treatment
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Heart disease or clotting disorders.
Spot the Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Because most Pulmonary Embolisms start as DVTs, recognising these early can prevent a serious emergency. See your doctor if you notice:
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling in one leg (usually the calf or thigh)
- Warmth, redness, or discolouration of the skin
- The leg feels heavy or tight.
Do not massage the leg. Seek medical advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Other Patient Pathway Posts
What to Expect After a Head Injury

Recovering After A Concussion

How to Care for a Child Who Has Croup
Choking: What You Can Do to Help

Understanding Your Headache & When to Seek Help
Understanding Burns
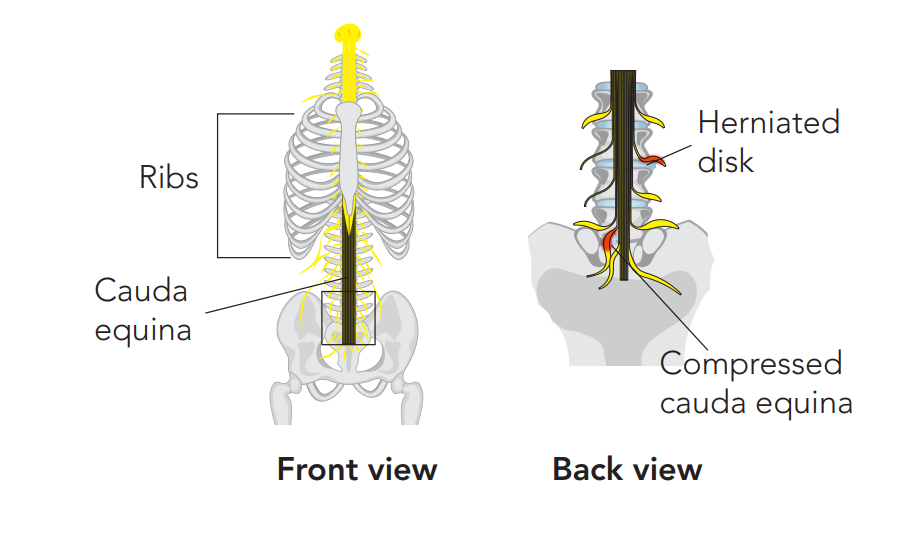
Recognising the Red Flags of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovering After Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovery From Back Pain

Pain Relief: Safe Use of Over-the-Counter Medications



