Your Cerebral Angiography Journey
 Download PDF
Download PDF
 Download PDF
Download PDF
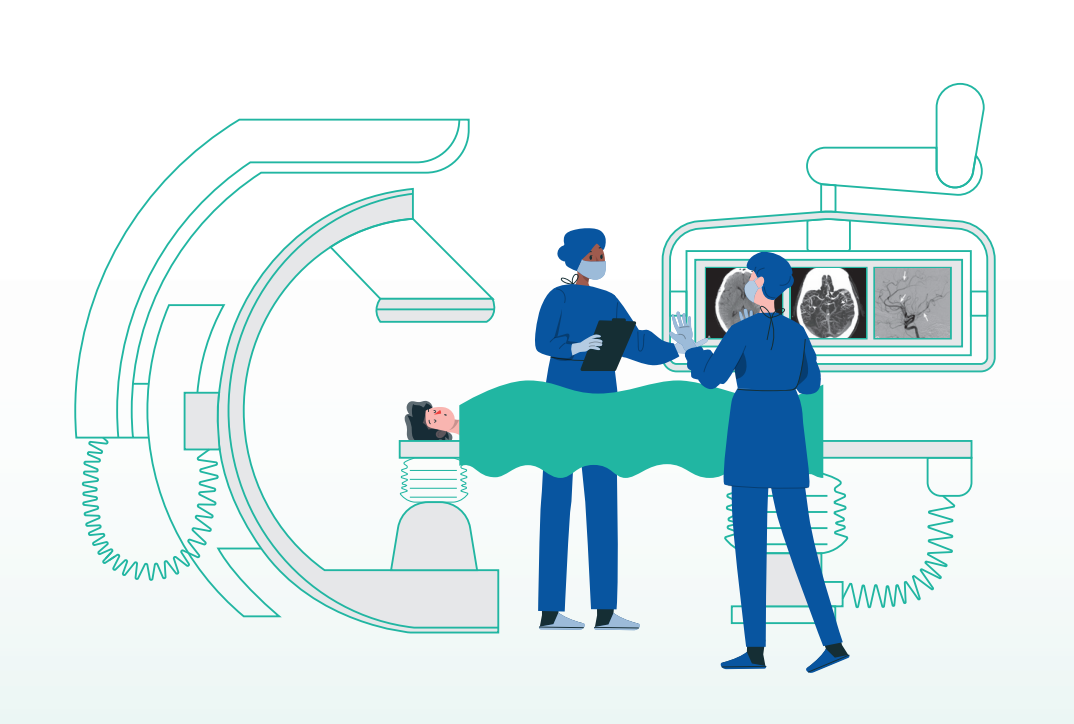
Your Cerebral Angiography Journey
We want to ensure that you receive the highest level of healthcare. This means keeping you educated and informed about what is involved in the different stages of your Cerebral Angiography. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak with your doctor or medical team.
Understanding Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral Angiography (also known as a cerebral arteriogram) is a diagnostic procedure that uses X-ray imaging and contrast dye to visualise the arteries and veins in your brain and neck.
It helps doctors detect and evaluate:
- Aneurysms (bulging or weakened blood vessel walls)
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
- Vessel narrowing or blockages (stenosis)
- Blood clots or stroke causes
- Bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Vessel involvement in brain tumours.
Reasons for Cerebral Angiography
This Test provides more detailed images than MRI or CT scans. It is often used when:
- Other imaging is unclear,
- A surgical or interventional procedure is being planned, or
- Treatment decisions depend on the precise blood vessel anatomy.
Preparing for Your Procedure
What to Tell Your Doctor
Before the test, inform your care team if:
- You are pregnant or may be pregnant
- You have allergies, especially to iodine, contrast dye, or shellfish
- You have kidney problems
- You are taking blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel)
- You have diabetes (especially if on metformin)
- You’ve had a reaction to contrast dye in the past.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
Your medical team will provide specific instructions, some of which are included below.
Details
Don’t eat or drink anything except water) for 6 hours before the test.
You may need to stop blood thinners 2–5 days in advance. Always follow your doctor’s guidance.
You may have kidney function or clotting tests before the procedure.
You may feel drowsy after the test. Do not drive yourself home; arrange for someone to accompany you.
Packing for the Hospital
Bring the following with you on the day:
- A list of all medications and allergies
- Government-issued ID
- Health insurance information
- Comfortable clothing (you’ll change into a gown).
Leave all valuables and jewellery at home.
The Day of the Procedure
On Arrival
- You’ll check in at the nurses station.
- A nurse will place an IV line in your arm for fluids and medications.
- You’ll change into a hospital gown.
Before the Procedure
- You’ll meet the anaesthetist and your medical team.
- You may receive a mild sedative to help you relax.
- Your vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen) will be monitored.
What to Expect During Cerebral Angiography
STEP 1: Catheter Insertion
- The doctor will clean and numb the area—usually your groin or wrist.
- A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery and guided up to the brain using X-ray images (fluoroscopy).
STEP 2: Contrast Dye Injection
- A special dye is injected through the catheter.
- You may feel a warm flush, metallic taste, or brief dizziness—this is normal and passes quickly.
- X-rays are taken in real-time to capture detailed views of your brain’s blood vessels.
STEP 3: Completion
- Once imaging is complete, the catheter is
gently removed. - Pressure is applied to the site for 10–20 minutes to stop bleeding.
- A small bandage or closure device is applied.
Recovery after Cerebral Angiography
In the Recovery Room
- You’ll be monitored for 4–6 hours.
- You’ll need to lie flat for a period to prevent bleeding at the insertion site.
- Nurses will check your blood pressure, pulse, and insertion site frequently.
- Most patients go home the same day. If additional treatment or monitoring is needed, you may be admitted.
Caring for Yourself at Home
What to Do/Watch For
Rest. Keep the bandage clean and dry. Drink fluids to help flush the dye from your system.
Mild bruising, soreness, or a small lump at the puncture site is normal.
Avoid heavy lifting, vigorous exercise, and long baths. Showering is okay.
Follow-up with your doctor to review results and plan next steps.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room if you notice:
- Bleeding or a rapidly growing lump at the catheter site
- Numbness, weakness, or coldness in your leg or arm
- Fever or chills
- Severe headache
- Vision changes or difficulty speaking
- Chest pain or shortness of breath.
Follow-Up Appointments
After the test:
- Your results will be reviewed by your neurologist or specialist;
- You may have a follow-up visit within 1–2 weeks; and
- Your doctor will discuss options if treatment (e.g., surgery, embolisation, or stenting), is needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Other Patient Pathway Posts
Pulmonary Embolism
What to Expect After a Head Injury

Recovering After A Concussion

How to Care for a Child Who Has Croup
Choking: What You Can Do to Help

Understanding Your Headache & When to Seek Help
Understanding Burns
Recognising the Red Flags of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovering After Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovery From Back Pain



