Your CT Scan Experience
 Download PDF
Download PDF
 Download PDF
Download PDF

Your CT Scan Experience
We want to ensure that you receive the highest level of healthcare. This means keeping you educated and informed about what is involved in the different stages of your diagnostic procedure. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak with your doctor or medical technician.
What is A CT Scan?
A CT (Computerised Tomography), or a CAT (Computerised Axial Tomography) Scan is a specialised X-ray test that gives the medical team a clearer picture of inside your body. It assists them with making medical decisions for your treatment.
Why is a CT Scan Needed?
You may need a CT Scan to:
- Give clear pictures of bones and soft tissues (such as muscles, organs, large blood vessels, the brain and nerves), which
an ordinary X-ray test cannot show; - Determine the cause of a stroke;
- Determine serious head injuries;
- Detect abnormalities in the body, such as tumours, abscesses, abnormal blood vessels and so on when they are suspected by symptoms or other tests;
- Give a surgeon a clear picture of an area of your body before certain types of surgery;
- Pinpoint the exact site of tumours prior
to radiation therapy; and - To help doctors find the right place to take tissue samples called biopsies.
What are the Risks of a CT Scan?
CT Scans use a very small amount of radiation, therefore the risk of radiation exposure is low. However, if you are pregnant or suspect you are
pregnant, please inform your physician. The medical team can work with the radiology team to reduce the risk of radiation to the fetus if a CT
Scan is still advised.
- If you have been diagnosed with any kidney issues, this must be discussed with your medical team.
- If you need a CT Scan with contrast dye, in rare cases there is a small risk of an allergic reaction to the dye. This is more likely if you are allergic or sensitive to medications, contrast dye, iodine, or shellfish.
- Contrast can assist in differentiating soft tissues and blood vessels on CT Scans. The result is a more detailed image of the organs and structures being examined.
- A CT Scan with contrast will require that you do a blood test prior to the CT Scan. The blood test (creatinine and maybe others, such as blood urea nitrogen) will check that your kidneys are functioning properly.
There are different types of contrasts.
- Intravenous (IV) Contrast
A nurse will insert an IV line into your hand or arm where the contrast (liquid) will flow into your vein. IV contrast is especially helpful when screening for infections, blood clots, tumours, or soft tissue abnormalities.
- Oral Contrast
You will be given 1.5-2 litres for most abdominal CT Scans. You must drink this contrast over the course of an hour and you will be asked to drink this while you are waiting for your CT Scan.
- Rectal Contrast
This will be inserted into your rectum by a nurse before your CT Scan.
Who will be involved in the CT Scan?
Your CT Scan will include a few team members.
Radiology Technician
The radiology technician will assist you onto the CT couch, position you correctly and start the CT Scan, as well as monitor your safety throughout the procedure.
Radiologist
This is the medical doctor who will report on the CT Scan.
Nurse
The nurse will assist the team at any point and insert an IV cannula if needed.
This is what you can expect when you come to Health City for a CT Scan.
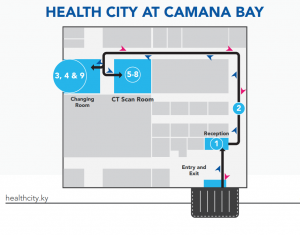
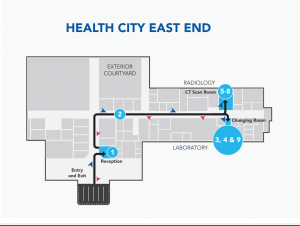
- When you arrive at Health City, you will check in at Reception.
- A member of the Health City team will escort you from the lobby to the diagnostic wing.
- The radiology technician will ask you to read and sign a consent document for the CT Scan. You will need to sign a second form if you require contrast. At this time, you will be asked to drink a certain amount of oral contrast (if necessary).
- You will be instructed to get changed into a patient gown and remove any items that may contain metal.
- All jewellery including watches
- Eyeglasses
- Hairpins/Barrettes containing metal
- Dentures
- Hearing aids
- Underwire bras
- The radiology team member will then accompany you to the CT room. The nurse will insert an IV cannula and administer the contrast (if necessary).
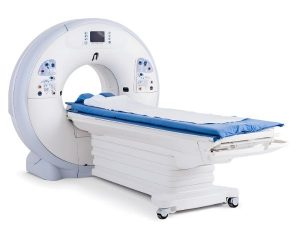
- The CT scanner looks like a thick, giant ring. Within the wall of the scanner there is an X-ray source and on the other side are
the X-ray detectors. You will be assisted onto the couch, which will slide into the CT scanner ring and stop on the part of your
body that needs scanned. - The X-ray within the ring rotates around your body, emitting thin X-ray beams that are detected by the X-ray detectors. Several cross-sectional images of the part of your body being investigated are made by the computer. The CT scanner can be a bit noisy but that’s just the movement of the machine. Your CT Scan appointment can last for up to 60 minutes. You will be on
the CT couch for 10 to 20 minutes. - Once the imaging has been completed, the radiology team member will assist you off the couch.
- You may get changed and leave the department/hospital. Your CT report will be sent to the ordering physician within 48
hours. Please ensure you have your follow-up appointment booked after.
Frequently Asked Questions
Other Patient Pathway Posts
Pulmonary Embolism
What to Expect After a Head Injury

Recovering After A Concussion

How to Care for a Child Who Has Croup
Choking: What You Can Do to Help

Understanding Your Headache & When to Seek Help
Understanding Burns
Recognising the Red Flags of Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovering After Cauda Equina Syndrome
Recovery From Back Pain



